HTML Id
The HTML id attribute is used to specify a unique id for an HTML element.
Using The id
Ther is some point we need to know about ID
- We can use this for one single and particular element. We can't use it twice.
- ID Specificity is 1,0,0 (This is hight). In order to replace it we can use an !important
- The syntax for id is: write a hash character (#), followed by an id name. Then, define the CSS properties within curly braces {}.
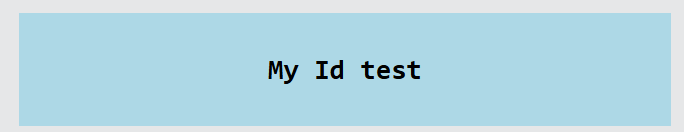
- In the following example, we have an <h1> element that points to the id name "myId". This <h1> element will be styled according to the #myId style definition in the head section:
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
#myId {
background-color: lightblue;
color: black;
padding: 40px;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 id="myId">My Id test</h1>
</body>
</html>Result:
Difference Between Class and ID 👇🏾
A class name can be used by multiple HTML elements, while an id name must only be used by one HTML element within the page:
HTML Bookmarks with ID and Links
- HTML bookmarks are used to allow readers to jump to specific parts of a webpage.
- can be useful if your page is very long.
- To use a bookmark, you must first create it, and then add a link to it.
- Then, when the link is clicked, the page will scroll to the location with the bookmark.
Example
<h2 id="myId">Go to page header</h2>Code preview is not apply
HTML Id Summary ✨
- The id attribute is used to specify a unique id for an HTML element
- The value of the id attribute must be unique within the HTML document
- The id attribute is used by CSS and JavaScript to style/select a specific element
- The value of the id attribute is case sensitive
- The id attribute is also used to create HTML bookmarks